 The Platinum Price Phenomenon: Understanding the Recent Surge and Future Outlook
The Platinum Price Phenomenon: Understanding the Recent Surge and Future Outlook
Platinum, often overshadowed by its more famous counterparts, gold and silver, has experienced a remarkable surge in value throughout 2025. The precious metal, prized for its rarity and diverse industrial applications, has seen its price climb to decade-high levels, captivating the attention of investors, industry analysts, and consumers alike. This dramatic rally is not a fleeting trend but rather a reflection of significant structural shifts in the global platinum market, driven by a confluence of supply constraints, robust demand, and shifting investment dynamics.
This comprehensive article delves into the factors propelling the platinum price to new heights, analyzing the intricate balance of supply and demand, the impact of geopolitical and economic forces, and the long-term outlook for this essential metal.
A Historical Perspective: Platinum’s Volatile Journey
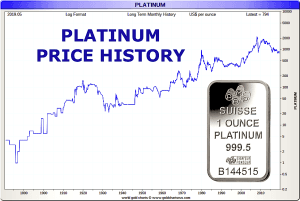
Platinum’s price history has been characterized by periods of intense volatility, often linked closely to its primary role in industrial applications, particularly in the automotive sector. Unlike gold, which primarily serves as a safe-haven asset, platinum’s value is deeply intertwined with global economic activity and manufacturing.
Over the past decade, platinum prices have experienced significant fluctuations. After reaching highs in the mid-2010s, the metal faced challenges due to oversupply concerns and the increasing focus on electric vehicles, which threatened the demand for internal combustion engine components. However, the narrative has fundamentally shifted in recent years.
As of mid-2025, platinum has emerged as a top-performing commodity, with some analysts reporting year-to-date gains exceeding 50%. This exceptional performance has narrowed the historical gap between platinum and gold, signaling a renewed appreciation for platinum’s fundamental value and its critical role in a transitioning global economy.
The Supply Squeeze: The Root of the Rally
The most potent catalyst for the recent platinum price surge is a persistent and worsening supply deficit. The platinum market is currently facing a projected shortfall of nearly one million ounces in 2025, a situation described by industry experts as a “structural” deficit rather than a temporary imbalance.
South Africa’s Dominance and Disruption
A crucial element of the supply challenge lies in South Africa, which accounts for approximately 80% of the world’s mined platinum output. Mining operations in the country have been severely hampered by a combination of factors, including power outages, logistical bottlenecks, excessive rainfall, and ongoing operational challenges. These disruptions have led to a substantial decline in refined production and a constrained project pipeline for new mines.
The structural inelasticity of platinum supply means that even significant price increases do not translate into immediate production gains. Developing a new platinum mine is a complex, capital-intensive process that can take eight to nine years to reach full capacity. Consequently, the market cannot quickly respond to the rising demand, leading to a tightening of available physical supply.
Challenges in Recycling
Compounding the issue is the constrained secondary supply from recycling, particularly from catalytic converters. While recycling is a vital source of platinum, recovery rates have been affected by extended vehicle lifespans and a decline in the number of end-of-life vehicles entering the recycling stream. This has further exacerbated the overall supply deficit.
Demand Drivers: Beyond the Auto Industry
While supply constraints have set the stage, surging demand across various sectors has provided the necessary momentum for the price rally.
The Automotive Catalyst: A Resurgent Force
The automotive industry remains the largest consumer of platinum, primarily for use in catalytic converters to reduce emissions in internal combustion engines. Despite the long-term trend towards electric vehicles, platinum demand in this sector remains robust due to several factors:
- Hybrid Vehicle Growth: Hybrid vehicles, which continue to utilize catalytic converters, are seeing increased adoption globally.
- Substitution Effect (Platinum for Palladium): Platinum is increasingly being used as a substitute for palladium in gasoline engine catalytic converters. As platinum has historically been priced lower than palladium, this substitution makes economic sense for manufacturers.
- Stricter Emission Standards: Global regulations on vehicle emissions are becoming increasingly stringent, driving the need for more efficient catalytic systems, which often rely on platinum.
The Hydrogen Economy and Green Technologies
A significant long-term driver for platinum demand is its crucial role in the emerging hydrogen economy. Platinum is a vital catalyst in fuel cells, which are essential for producing clean hydrogen and powering hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). As nations worldwide prioritize decarbonization and green energy transitions, the demand for platinum in these applications is expected to grow substantially.
The Chinese Jewelry Market: A Cultural Shift
The Chinese jewelry market has also emerged as a powerful driver of platinum demand. In response to historically high gold prices, Chinese consumers are increasingly turning to platinum jewelry. This shift in consumer preference has led to a significant uptick in platinum imports and a notable increase in platinum jewelry fabrication.
Investment Trends and Market Dynamics
The rise in platinum prices has also been fueled by a renewed interest from the investment community.
Investor Rotation and “Gold Fatigue”
With gold trading at historically high levels, some investors are experiencing “gold fatigue” and seeking undervalued precious metals. Platinum, which had underperformed gold for nearly a decade, has emerged as an attractive alternative. This rotation of capital into platinum-backed exchange-traded funds (ETFs), bars, and coins has added significant momentum to the price rally.
Geopolitical and Economic Influence
While platinum is primarily an industrial metal, its price is not immune to broader geopolitical and economic forces. Global economic uncertainty, inflation concerns, and shifting monetary policies have influenced investor behavior. Concerns over potential trade restrictions and disruptions in major producing regions have also contributed to price volatility and heightened market tightness, reflected in elevated lease rates for the metal.
The Future of Platinum: Deficits and Opportunities
The consensus among analysts is that the structural deficits in the platinum market are likely to persist for the foreseeable future. The World Platinum Investment Council (WPIC) projects continued annual deficits through 2029.
Potential Headwinds
Despite the bullish outlook, the platinum market faces potential headwinds. The most significant is the risk of “price-induced demand destruction.” If platinum prices rise too rapidly, industrial buyers, particularly in the automotive and glass sectors, may seek to reduce their consumption or find alternative materials. Furthermore, while the supply deficit is real, substantial above-ground inventories of platinum exist, which could act as a buffer against shortages and a psychological ceiling on runaway price increases.
A Compelling Investment Case
However, the long-term investment case for platinum remains compelling. Its critical role in environmental technologies, including catalytic converters and the hydrogen economy, ensures continued industrial relevance. The persistent supply challenges in South Africa and the rarity of the metal suggest that the market will remain undersupplied, providing a strong foundation for future price appreciation.
Investors and industries alike are closely watching the platinum market. The recent surge is not merely a cyclical upturn but potentially the beginning of a new era for platinum, driven by its indispensability in a world increasingly focused on sustainable technologies and a supply chain facing fundamental challenges. As the global transition to a cleaner energy future accelerates, platinum’s role—and its value—is set to become even more prominent.

 The Platinum Price Phenomenon: Understanding the Recent Surge and Future Outlook
The Platinum Price Phenomenon: Understanding the Recent Surge and Future Outlook